Crystal Lattice Visualizer
This is an interactive tool that visualizes various crystal lattice structures in both real and reciprocal space. You can explore Simple Cubic (SC), Body-Centered Cubic (BCC), Face-Centered Cubic (FCC), Diamond, and Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) structures.
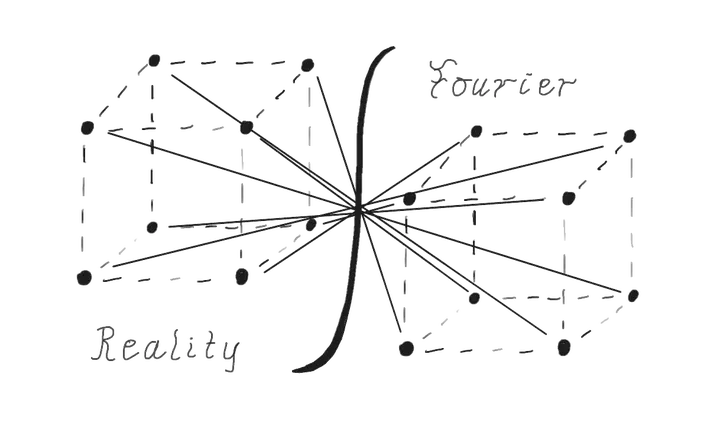
The elegance and power of Fourier’s famous integral transformation was probably the single most fascinating thing which I got to know during my studies of electrical engineering. A theorist might note that his function is only a special case of LaPlace transformation, but when it comes to applications, Fourier’s transform outshines it manyfold. The use of the impulse-/reciprocal space in material science is one particularly fascinating application, as it creates beautiful 3D structures, which help explain the real world.
Features
- Visualize common crystal lattice structures in 3D
- Toggle between real space and reciprocal space views
- Adjust lattice constants
- Customize unit cell count and display options
- View special k-points in reciprocal space (Brillouin zone)
- Rotate and zoom the 3D models using mouse controls
Real Space Lattice
Reciprocal Space Lattice
Lattice Information
Lattice Type: Simple Cubic (SC)
Lattice Constant: 1.00 Å
Reciprocal Lattice Constant: 6.28 Å⁻¹
Brillouin Zone: Cubic
How It Works
The visualization uses Three.js, a JavaScript 3D library, to render the crystal structures in real-time. The crystal lattice structures are generated programmatically based on the selected parameters.
In the real space view, you can see the actual arrangement of atoms in the crystal structure. The reciprocal space view (also known as k-space) represents the Fourier transform of the real space lattice, which is particularly useful for understanding X-ray diffraction patterns and electron band structures in solid-state physics.
Technical Details
This visualization is built with vanilla JavaScript and Three.js for 3D rendering. The Brillouin zone boundaries (shown in green in the reciprocal space view) represent the first Brillouin zone, which is the Wigner-Seitz cell of the reciprocal lattice.
The colored points in reciprocal space (when labels are enabled) indicate high-symmetry points that are commonly used as reference points when describing electronic band structures:
- Γ (Gamma): Center of the Brillouin zone (green)
- X: Face centers in cubic lattices (red)
- L: Body centers in FCC lattice (blue)
- K: Special points along certain high-symmetry directions (magenta)
Feel free to explore different crystal structures by adjusting the controls!